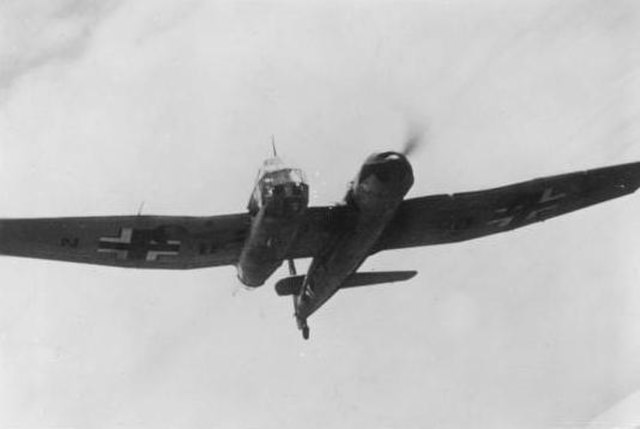
The Blohm & Voss BV 141 was designed as a tactical reconnaissance aircraft. While passed over by the German Air Ministry for the Focke-Wulf Fw 189 Uhu, it became the better known of the two, due to its asymmetrical body. The aircraft’s unusual design made it appear as though it shouldn’t have been able to safely take to the air. However, tests showed it was able to fly without issue.
In 1937, two years prior to the start of World War II, the Air Ministry issued a call to German manufacturers for a single-engine reconnaissance aircraft. A number of companies submitted designs, with the favorable option initially being the Arado Ar 198. When the prototype proved to be unsuccessful, however, the two-engine Focke-Wulf Fw 189 Uhu was chosen, despite not meeting the single-engine requirement laid out by the Luftwaffe.
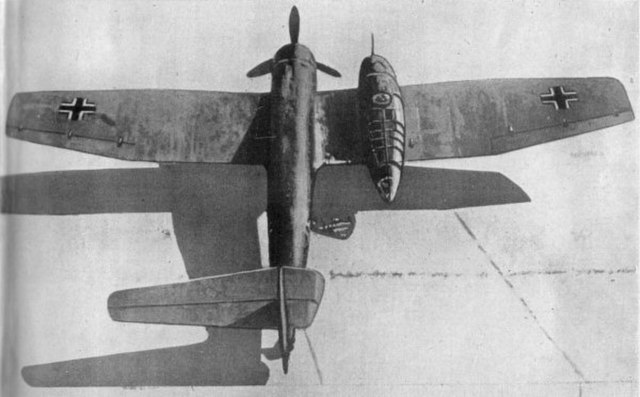
Privately, Blohm & Voss began working on their own design for a new reconnaissance aircraft, resulting in the creation of the BV 141. Developed by German military aircraft designer Richard Vogt, it featured a rather unusual asymmetrical design that made it appear lopsided both on the ground and from the air.
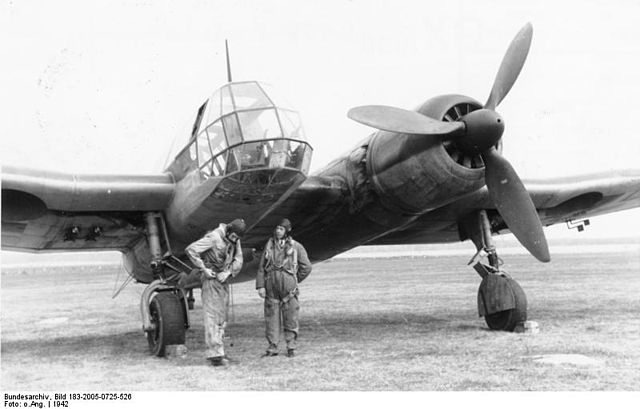

In terms of armaments, the Blohm & Voss BV 141 featured a total of four machine guns – two rear-mounted flexible 7.92 mm MG 15s and two fixed-forward 7.92 mm MG 17s. The aircraft was also equipped to carry four SC 50 bombs.
Initially, the BV 141 was powered by a BMW 132N radial engine, which ran the aircraft’s three-blade propeller system. This was later upgraded to the more powerful BMW 801, which provided it with a range of 1,200 miles. The BV 141’s maximum speed was 229 MPH at sea level and 272 MPH at an altitude of 5,000 meters.
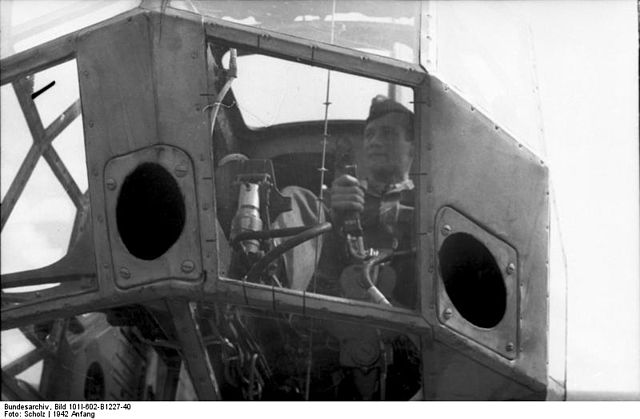

Three prototypes and an additional five BV 141As were produced for evaluation by the Air Ministry. The aircraft’s development wasn’t supported by many, but did have an advocate in Generaloberst Ernst Udet, a World War I veteran and the director of the Air Ministry’s research and development section.
The BMW 801 engine was installed in the BV 141B after the Air Ministry determined the initial version of the aircraft was underpowered. However, by the time the “B” variant was produced, the Fw 189 had already entered production. As well, the BMW 801 was needed for more proven aircraft, such as the Focke-Wulf Fw 190 Würger, lessening the likelihood the BV 141 would have entered full-scale service.

